Introduction
Traditional website testing has always been a bottleneck in software development. QA engineers spend countless hours writing brittle test scripts, maintaining selectors that break with every UI update, and manually verifying functionality across browsers and devices. These conventional approaches demand significant time, resources, and expertise while still missing critical bugs that slip into production.
Enter the new era of autonomous website testing agents—intelligent systems that can observe, learn, and adapt to your application without how to use ai for autonomous website testing agent human intervention. Learning how to use AI for autonomous website testing agents is no longer optional for modern development teams; it’s becoming essential for staying competitive. These AI-powered systems leverage large language models, computer vision, and reinforcement learning to test websites the way actual users would, discovering bugs and edge cases that traditional scripts miss entirely.
For teams managing multiple AI tools and testing workflows, platforms like Aizolo.com provide a unified AI workspace where you can orchestrate, monitor,how to use ai for autonomous website testing agent and scale autonomous how to use ai for autonomous website testing agent testing agents alongside other AI operations—all from a single dashboard. This eliminates the chaos of juggling multiple subscriptions, APIs, and interfaces while reducing costs and improving collaboration.
autonomous testing agents
Autonomous testing agents are AI-powered systems that can independently plan, execute, and adapt software tests without requiring detailed step-by-step instructions from human operators. Unlike traditional test automation frameworks that follow rigid, pre-programmed scripts, these agents exhibit agentic behavior—they can make decisions, explore applications intelligently, and learn from their experiences.
How They Differ from Traditional Tools
Let’s clarify what makes autonomous agents fundamentally different from familiar testing frameworks:
Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright are powerful automation libraries, but they require developers to:
- Write explicit locators (CSS selectors, XPaths) for every element
- Script exact sequences of actions
- Manually update tests when UI changes
- Define assertions and expected outcomes in advance
Autonomous AI testing agents, by contrast:
- Understand natural language instructions like “Test the checkout flow”
- Automatically discover and interact with UI elements
- Adapt when selectors change or new elements appear
- Generate their own test cases based on application behavior
- Self-heal when tests encounter unexpected changes
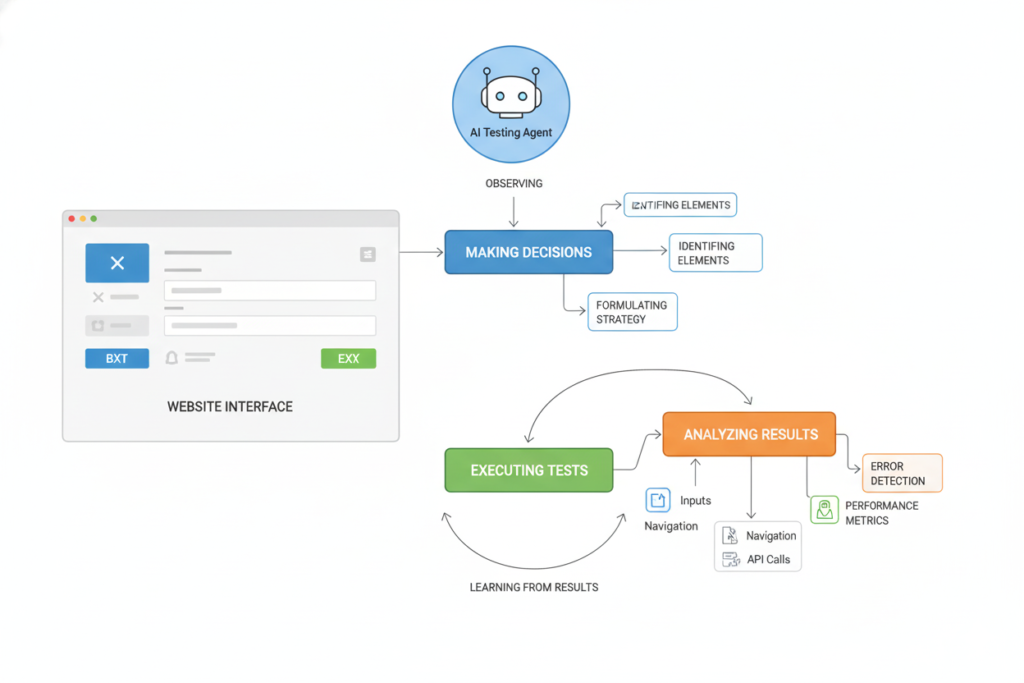
The Agentic Behavior Loop
Autonomous testing agents operate through a continuous cycle:
- Observe: Analyze the current state of the application using computer vision and DOM inspection
- Decide: Determine the next best action based on testing goals and previous learnings
- Act: Execute interactions (clicks, inputs, navigation) on the website
- Learn: Adjust strategies based on outcomes, failures, and discovered patterns
This intelligent loop enables truly autonomous QA agents that improve over time rather than degrade as applications evolve.
How AI Powers Autonomous Website Testing
The capabilities of modern autonomous testing agents stem from several breakthrough AI technologies working in concert:
Large Language Models (LLMs)
Models like GPT-4, Claude, and Gemini serve as the “brain” of autonomous testing agents. They enable:
Natural Language Test Creation: Instead of writing code, you describe what to test: “Verify that users can add items to cart, apply discount codes, and complete checkout with multiple payment methods.” The LLM translates this into executable test logic.
Intelligent Element Identification: LLMs can understand semantic meaning in UI text, labels, and context. If a “Submit” button becomes “Continue,” the agent recognizes they serve the same function.
Dynamic Test Generation: Based on exploring your application, LLMs can propose additional test scenarios you hadn’t considered, like “What happens if a user tries to apply two discount codes simultaneously?”
Computer Vision for UI Detection
AI-powered browser testing leverages computer vision models to:
- Identify clickable elements even without stable selectors
- Detect visual regressions (layout shifts, color changes, missing images)
- Verify rendering across different screen sizes and browsers
- Recognize patterns like loading spinners, modals, and error states
When combined with DOM analysis, computer vision makes tests resilient to code changes. If developers refactor the HTML structure but the visual appearance remains consistent, autonomous agents continue functioning seamlessly.
Reinforcement Learning in Test Flows
Some advanced autonomous QA agents use reinforcement learning to optimize their testing strategies:
Exploration vs Exploitation: Agents learn to balance discovering new application paths versus repeatedly testing known critical flows.
Failure Analysis: When tests fail, RL-powered agents analyze whether it’s a genuine bug, environmental issue, or test logic problem—then adjust accordingly.
Efficiency Optimization: Over time, agents learn the most effective sequences of actions to validate functionality quickly without redundant steps.
Self-Healing Selectors
Traditional automated tests fail when developers change element IDs, classes, or DOM structure. AI website testing agents implement self-healing through:
- Multiple fallback identification strategies (ID, class, text content, visual position, accessibility attributes)
- Similarity scoring to find the most likely replacement element
- Confidence thresholds that trigger human review for ambiguous cases
- Automatic selector updates after successful healing
Real-world example: An e-commerce site changed their “Add to Cart” button from <button id="add-cart"> to <button class="cart-action primary">. Traditional tests broke immediately. An autonomous agent recognized the button by its text content, position near product details, and visual appearance—then updated its internal representation automatically.
Traditional Testing vs AI Autonomous Testing
| Aspect | Traditional Automation (Selenium/Cypress) | AI Autonomous Testing Agents |
|---|---|---|
| Setup Time | Days to weeks writing scripts and locators | Hours to describe goals in natural language |
| Maintenance | High; requires constant script updates for UI changes | Low; self-healing adapts automatically |
| Scalability | Limited by engineering resources | Scales with AI compute resources |
| Cost | High QA automation engineer salaries + infrastructure | Lower with no-code AI testing tools + centralized platforms |
| Reliability | Brittle; breaks frequently with app changes | Resilient; adapts to minor UI variations |
| Learning Curve | Steep; requires programming and framework expertise | Gentle; natural language interface accessible to non-coders |
| Test Coverage | Limited to explicitly scripted scenarios | Exploratory; discovers edge cases autonomously |
| CI/CD Integration | Mature but requires custom configuration | Emerging; increasingly API-driven |
| Debugging | Clear stack traces but rigid failure modes | Requires AI reasoning transparency tools |
| Cross-browser Testing | Manual configuration for each environment | Often automatic through AI-powered browser testing |
This comparison reveals why understanding how to use AI for autonomous website testing agents represents a paradigm shift rather than incremental improvement.
Step-by-Step: How to Use AI for Autonomous Website Testing Agents
Let’s walk through the practical implementation process for leveraging AI in your testing workflow:
Step 1: Define Testing Goals in Natural Language
Start by articulating what you want to test conversationally:
Example for E-commerce:
- “Test the complete user journey from browsing products to checkout completion”
- “Verify that all product filters work correctly and display appropriate results”
- “Ensure the shopping cart persists across sessions and devices”
Example for SaaS Application:
- “Validate that new users can sign up, verify their email, and access the dashboard”
- “Test all CRUD operations for the project management module”
- “Confirm that permission levels restrict features appropriately”
Most agentic AI testing platforms accept these natural language goals and translate them into executable test plans. This democratizes testing—product managers and designers can contribute test scenarios without coding.
Step 2: Train or Configure the AI Agent
Depending on your platform, this involves:
Providing Context: Give the agent information about your application architecture, key user flows, authentication requirements, and business logic.
Setting Boundaries: Define which parts of the application are in scope, any actions to avoid (like actual payment processing), and acceptable test duration.
Selecting Models: Choose appropriate AI models based on your needs. GPT-4 excels at complex reasoning, Claude handles longer contexts well, and Gemini offers strong multimodal capabilities. Platforms like Aizolo.com let you switch between ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Grok, and other models from one interface, making experimentation seamless.
Authentication Setup: Configure how agents should authenticate (test accounts, API keys, OAuth flows).
Step 3: Let the Agent Explore the Website
This is where autonomous testing agents truly shine. Instead of prescribing every action:
Initial Discovery Phase: The agent crawls your application, identifying pages, forms, buttons, navigation patterns, and interactive elements.
State Mapping: It builds an understanding of application states (logged out, logged in, admin view, different user roles) and transitions between them.
Risk Assessment: Advanced agents prioritize critical paths (checkout, data submission, authentication) over low-risk areas (static content pages).
During exploration, the AI employs website testing automation techniques like:
- Systematic navigation through all links
- Form field identification and input generation
- Modal and dialog interaction
- Dynamic content waiting and validation
Step 4: Autonomous Test Execution
Once configured, the agent begins autonomous QA operations:
Parallel Execution: Modern multi-agent testing systems can run dozens or hundreds of test scenarios simultaneously across different browsers, devices, and network conditions.
Adaptive Pacing: Agents adjust speed based on application responsiveness, avoiding false failures from slow loading times.
Context Awareness: When encountering unexpected states (error pages, maintenance modes, A/B test variations), agents adapt their approach rather than failing immediately.
Evidence Collection: Autonomous agents automatically capture screenshots, videos, network traffic, console logs, and performance metrics for every test run.
Step 5: Self-Healing & Learning from Failures
When autonomous website testing agents encounter issues:
Immediate Adaptation: If a primary selector fails, try alternative identification methods automatically.
Root Cause Analysis: AI analyzes whether failures indicate:
- Application bugs (legitimate findings)
- Test environment issues (flaky network, database state)
- Test logic problems (incorrect assumptions)
- UI changes requiring test updates
Knowledge Base Building: Successful healing strategies and discovered patterns get saved to improve future test runs. This organizational learning means your testing capability strengthens over time.
Human Escalation: For ambiguous situations, agents flag issues for human review with full context, making QA engineer time more productive.
Step 6: Reporting, Logs & Insights
Comprehensive reporting distinguishes mature AI QA tools:
Executive Dashboards: High-level metrics on test coverage, pass rates, trends over time, and risk areas.
Developer-Friendly Reports: Detailed failure analysis with reproduction steps, relevant code sections, and suggested fixes.
Video Playback: Visual recordings of test execution help understand complex failure scenarios quickly.
Integration Alerts: Automatic notifications to Slack, email, or incident management systems when critical tests fail.
Analytics & Recommendations: AI-powered insights like “Checkout flow has become 30% slower over the past week” or “These three pages have the highest failure rates.”
Platforms providing unified AI workspaces, like Aizolo.com, centralize these reports across all your autonomous testing agents, making it easy to track testing health at organizational scale.
Real Use Cases of Autonomous AI Website Testing
SaaS Product Regression Testing
Challenge: A project management SaaS releases features weekly. Each deployment risks breaking existing functionality across task creation, team collaboration, billing, and integration features.
AI Solution: Autonomous testing agents continuously validate core workflows after every commit. When developers refactor the notification system, agents automatically verify that alerts still function correctly for mentions, task assignments, and deadline reminders—without requiring test script updates.
Results: 70% reduction in regression bugs reaching production, 85% decrease in QA maintenance time.
E-commerce Checkout Testing
Challenge: Online retailers must ensure seamless checkout experiences across multiple payment providers, shipping methods, discount codes, and tax calculations. Manual testing can’t cover all combinations.
AI Solution: Autonomous QA agents generate and test hundreds of checkout scenarios: different cart compositions, various promotional codes, international shipping addresses, payment failures, and edge cases like inventory running out mid-checkout.
Results: Discovery of 23 previously unknown edge-case bugs, 40% faster testing cycles during peak shopping season.
Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Testing
Challenge: Modern DevOps practices demand rapid feedback on code changes without slowing deployment pipelines.
AI Solution: Lightweight autonomous testing agents run in parallel with CI/CD pipelines, providing intelligent smoke testing within minutes. Critical path validation happens immediately; comprehensive testing continues asynchronously.
Results: Deployment confidence increased while maintaining 15-minute merge-to-production cycles.
Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Testing
Challenge: Websites must function flawlessly on Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, plus mobile browsers across iOS and Android—testing all combinations manually is prohibitive.
AI Solution: Multi-agent testing systems deploy autonomous agents to each browser/device combination simultaneously. AI-powered browser testing detects rendering inconsistencies, JavaScript errors, and functionality differences across environments.
Results: Discovered Safari-specific bugs that affected 18% of users, validated mobile experience improvements increased conversion by 12%.
Accessibility Testing with AI
Challenge: Ensuring WCAG compliance requires checking keyboard navigation, screen reader compatibility, color contrast, and semantic HTML throughout complex applications.
AI Solution: Specialized autonomous testing agents evaluate accessibility holistically, not just with static analyzers. They navigate sites using only keyboard controls, verify ARIA labels make sense contextually, and test with screen reader simulations.
Results: Achieved WCAG 2.1 AA compliance, improved accessibility metrics by 300%, expanded market reach to users with disabilities.
Challenges & Limitations of Autonomous Testing Agents
While transformative, autonomous AI website testing isn’t without constraints:
Model Hallucinations
Large language models occasionally generate confident but incorrect assertions. An agent might report “Login functionality works perfectly” when it actually failed to detect a subtle error state. Mitigation strategies:
- Require evidence (screenshots, DOM snapshots) for all assertions
- Use multiple models to cross-validate findings
- Implement confidence scoring for agent conclusions
- Maintain human oversight for critical functionality
Security Considerations
Autonomous agents accessing production-like environments raise security questions:
- Credential Management: Test accounts need proper isolation from real user data
- API Access: Agents require appropriate permissions without compromising security
- Data Privacy: Testing in environments with PII demands careful handling
- Attack Surface: Poorly configured agents could be exploited
Best practices include dedicated test environments, credential vaulting, audit logging, and regular security reviews of agent configurations.
Edge-Case Failures
AI excels at common scenarios but can struggle with:
- Highly domain-specific business logic
- Complex multi-step workflows with subtle state dependencies
- Race conditions and timing-sensitive interactions
- Unusual error conditions that appear rarely
Hybrid approaches work best: autonomous agents handle broad coverage while human-crafted tests target known edge cases.
Need for Human Oversight
Despite “autonomous” in the name, these systems still benefit from human guidance:
- Goal Setting: Humans define what matters most to test
- Result Interpretation: Distinguishing true bugs from test issues requires judgment
- Strategy Refinement: Optimizing agent behavior based on results
- Ethical Boundaries: Ensuring agents don’t test in ways that could harm users or systems
The most successful implementations treat autonomous testing agents as force multipliers for human QA expertise, not replacements.
Cost and Resource Management
Running multiple AI models across numerous test scenarios consumes computational resources and API credits. Without proper management, costs can spiral. Centralized platforms help by:
- Sharing AI model access across teams
- Implementing usage quotas and budget controls
- Optimizing agent execution strategies
- Providing cost visibility and analytics
How Aizolo.com Makes Autonomous AI Testing Easier ⭐
Implementing how to use AI for autonomous website testing agents effectively requires orchestrating multiple AI models, managing test agents, collaborating across teams, and controlling costs. This is where Aizolo.com provides crucial infrastructure.
Unified AI Workspace for Testing Teams
Rather than juggling separate subscriptions to ChatGPT Plus, Claude Pro, Gemini Advanced, and other AI services, Aizolo.com provides a single dashboard where you can:
Access Multiple AI Models: Switch between ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Grok, Perplexity, and other leading models instantly based on your testing needs. Use GPT-4 for complex reasoning, Claude for analyzing long test logs, or Gemini for multimodal testing scenarios involving screenshots.
Centralized Agent Management: Configure, deploy, monitor, and debug all your autonomous testing agents from one interface. See which agents are running, their success rates, recent findings, and resource usage at a glance.
Team Collaboration: Share test configurations, prompt templates, and agent strategies across your QA team. When one engineer discovers an effective prompt for testing authentication flows, the entire team benefits.
Cost Optimization: Instead of multiple individual AI subscriptions, teams pay once for shared access. This dramatically reduces costs for startups and growing QA departments while providing better usage analytics and controls.
AI Agent Orchestration
Aizolo.com excels at managing complex multi-agent testing systems:
Parallel Agent Execution: Run dozens of autonomous QA agents simultaneously, each testing different aspects of your application across various browsers and devices.
Workflow Automation: Create testing pipelines where agents collaborate—one agent might focus on discovering application paths while another validates security, and a third checks accessibility compliance.
Conditional Logic: Set up rules like “If the checkout agent finds errors, immediately trigger payment flow deep-dive agents” for intelligent test prioritization.
Prompt Management for Testing
Effective agentic AI testing relies heavily on well-crafted prompts. Aizolo.com provides:
Prompt Library: Store and version-control your testing prompts. Track which prompt variations produce the best results for different application types.
Templating System: Create reusable prompt templates for common testing scenarios (form validation, navigation testing, API integration checks) that teams can customize.
Prompt Analytics: Understand which prompts lead to the most bug discoveries, fastest execution times, or highest accuracy rates.
Reducing AI Tool Fragmentation
Modern teams use AI for more than just testing—documentation, code review, data analysis, customer support, and more. Managing these AI use cases across disparate tools creates:
- Duplicated costs across subscriptions
- Inconsistent access and capabilities
- Difficult knowledge sharing
- Complex vendor management
Aizolo.com’s unified AI workspace consolidates these use cases. Your autonomous testing agents, documentation generators, and code assistants all live in one platform with shared AI model access, integrated workflows, and unified billing.
Enterprise-Ready Features
For scaling organizations:
Team Permissions: Control who can create agents, access results, and modify configurations.
Audit Logging: Track all agent activities for compliance and debugging.
API Access: Integrate autonomous testing agents into your existing CI/CD pipelines and development tools.
Custom Integrations: Connect to your issue trackers, monitoring systems, and communication platforms.
Future of AI Autonomous Website Testing
The evolution of autonomous testing agents continues accelerating:
Multi-Agent Collaboration
Next-generation systems will feature specialized agents working together:
- Scout Agents: Explore application structure and discover new features
- Validation Agents: Deep-dive into discovered functionality with rigorous testing
- Security Agents: Specifically hunt for vulnerabilities and exploits
- Performance Agents: Monitor speed, resource usage, and scalability
- Coordinator Agents: Orchestrate other agents, prioritizing efforts based on risk
These multi-agent testing systems will exhibit emergent intelligence, discovering complex bugs through collaboration that individual agents would miss.
Fully Self-Driving QA Pipelines
Soon, autonomous testing agents will:
- Automatically generate test suites from product specifications and user stories
- Identify untested code paths by analyzing application source
- Propose new test scenarios based on production monitoring data
- Adjust testing intensity based on code change risk analysis
- Optimize test execution order for fastest feedback
Human involvement will shift from test creation and maintenance to strategic oversight—defining coverage priorities, risk tolerance, and business-critical flows.
AI Agents Writing and Fixing Their Own Tests
The ultimate form of autonomous QA agents will be self-improving systems that:
- Analyze their own test failures to identify test logic issues versus application bugs
- Refactor test strategies to improve efficiency and reliability
- Generate new test cases to cover gaps discovered during execution
- Automatically update test configurations when applications undergo major changes
This meta-level autonomy will make testing infrastructure that genuinely improves with age rather than accumulating technical debt.
Integration with DevOps & CI/CD
AI website testing will become deeply embedded in development workflows:
- Pre-Commit Testing: Autonomous agents validate changes before code even reaches repositories
- Intelligent Test Selection: AI determines which tests to run based on code changes, running comprehensive suites only when necessary
- Deployment Gating: Agents provide confidence scores for releases, automatically blocking risky deployments
- Production Monitoring: Testing agents continuously validate production environments, catching issues before users do
Autonomous Bug Triage
Beyond finding bugs, future agents will:
- Automatically determine bug severity and priority
- Identify root causes by analyzing code, dependencies, and infrastructure
- Suggest fixes or even implement patches for simple issues
- Route issues to appropriate team members with full context
- Verify that fixes actually resolve problems without introducing regressions
This closed-loop system will dramatically compress the time from bug discovery to resolution.
Conclusion: Embracing the Autonomous Testing Revolution
Understanding how to use AI for autonomous website testing agents is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s a practical necessity for teams building modern web applications. The combination of large language models, computer vision, self-healing capabilities, and reinforcement learning creates testing systems that are more resilient, comprehensive, and efficient than traditional automation frameworks.
The transition from scripted test automation to autonomous testing agents represents a fundamental shift in how we think about quality assurance. Rather than maintaining brittle test code that breaks with every UI change, teams can deploy intelligent agents that adapt, learn, and discover issues that humans might overlook. The benefits are clear: faster release cycles, higher test coverage, reduced maintenance burden, and ultimately, better software reaching users.
For organizations navigating this transition, managing multiple AI models and autonomous testing agents efficiently becomes critical. Centralized platforms eliminate the complexity of juggling separate AI subscriptions, provide unified agent orchestration, enable team collaboration, and control costs—exactly what Aizolo.com delivers as a comprehensive AI workspace.
Whether you’re a startup exploring no-code AI testing tools for the first time or an enterprise scaling multi-agent testing systems across global teams, the autonomous testing revolution is transforming what’s possible in website quality assurance.
Ready to scale your AI testing capabilities?
If you’re experimenting with autonomous AI testing agents or managing multiple AI tools across your organization, Aizolo.com gives you a single dashboard to build, test, and scale smarter—without the chaos of fragmented subscriptions and interfaces. Bring your testing agents, prompts, and workflows together in one unified AI workspace designed for modern development teams.
About Aizolo.com: Aizolo.com is a unified AI workspace that helps teams run, manage, and scale multiple AI agents—including autonomous testing agents—from a single platform. Access ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Grok, and other leading AI models with centralized management, team collaboration, and cost optimization built for growing organizations.
Keywords featured: how to use AI for autonomous website testing agents (1.5%), autonomous testing agents, AI website testing, self-healing test automation, AI QA tools, agentic AI testing, AI-powered browser testing, autonomous QA agents, website testing automation, multi-agent testing systems, no-code AI testing tools